The growth of the electronic commerce industry has reshaped how businesses generate revenue. Unlike traditional retail, online commerce allows companies to monetize products and services in multiple ways, often combining several revenue models at once.
Understanding these revenue models is essential for building profitable and scalable electronic commerce businesses. The right model can determine pricing strategy, customer acquisition costs, and long-term sustainability.
Why Revenue Models Matter in Electronic Commerce
A revenue model defines how an electronic commerce business earns money. It influences nearly every financial decision, from marketing spend to inventory planning.
A strong revenue model helps businesses:
-
Predict income more accurately
-
Improve cash flow stability
-
Scale operations efficiently
-
Adapt to market changes
Successful e-commerce companies design revenue models that align with customer behavior and business goals.
Product Sales: The Foundation of E-Commerce Revenue
Direct product sales remain the most common revenue model in the electronic commerce industry. Businesses sell physical or digital products through online platforms.
Key advantages:
-
Simple and familiar structure
-
Clear pricing strategy
-
Immediate revenue generation
However, margins depend heavily on sourcing, logistics, and marketing efficiency. Many businesses combine product sales with other models to improve profitability.
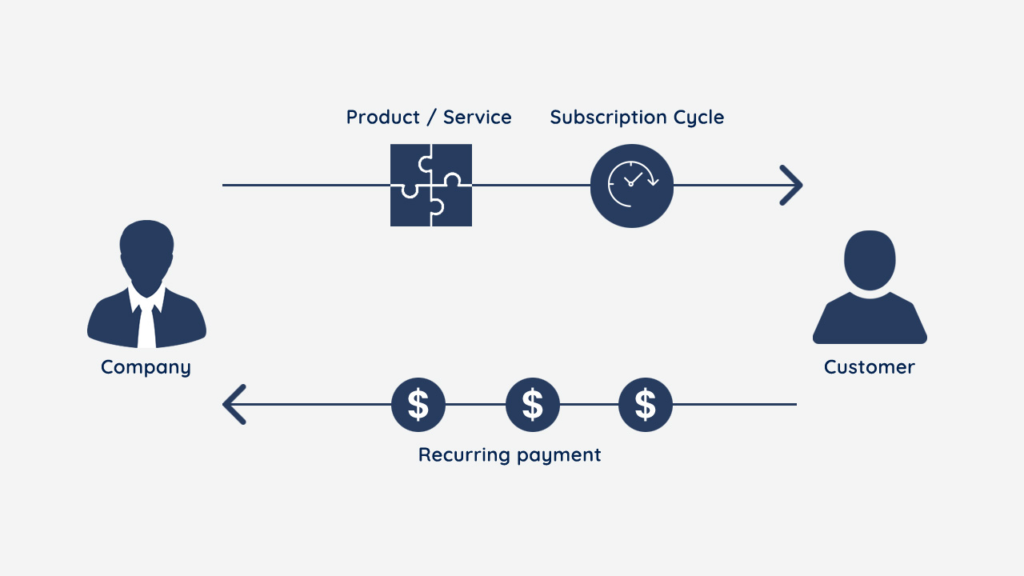
Subscription-Based Revenue Models
Subscriptions have become increasingly popular in modern e commerce businesses. Customers pay recurring fees for continued access to products or services.
Common subscription examples:
-
Monthly product deliveries
-
Digital memberships
-
Software-as-a-service offerings
-
Premium content access
Subscriptions create predictable income and improve customer lifetime value, making them attractive for long-term growth.
Marketplace and Commission-Based Models
Marketplace platforms connect buyers and sellers while earning a commission on each transaction. This model reduces inventory risk for the platform owner.
Why marketplaces scale well:
-
Low upfront inventory costs
-
Revenue grows with transaction volume
-
Diverse product offerings
Commission-based models are widely used across the electronic commerce industry due to their scalability.
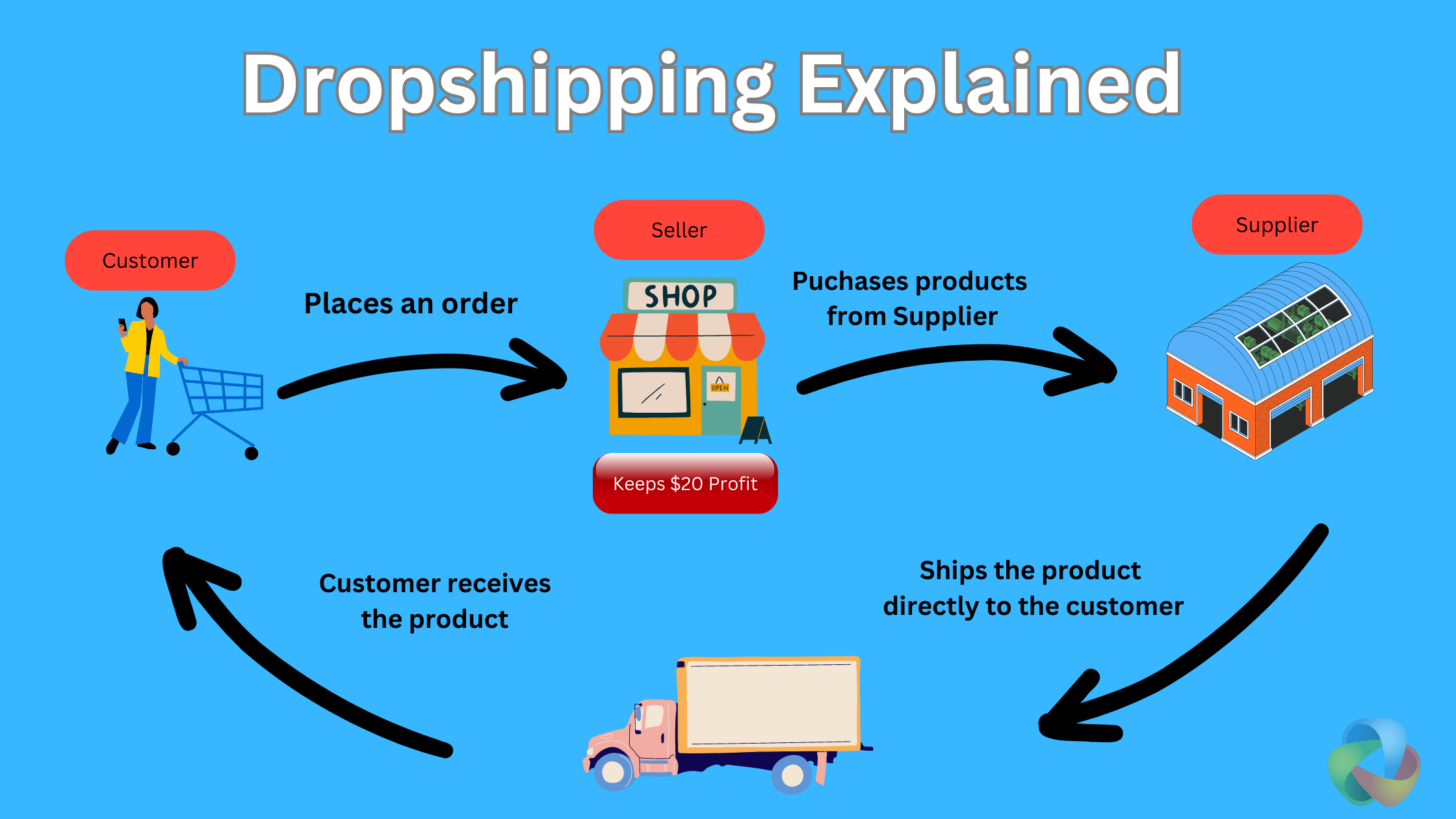
Dropshipping and On-Demand Fulfillment
Dropshipping allows businesses to sell products without holding inventory. Orders are fulfilled directly by suppliers.
Benefits include:
-
Lower startup costs
-
Reduced inventory risk
-
Flexible product testing
While margins can be thinner, dropshipping is popular among startups entering the electronic commerce business space.
Digital Products and Licensing
Digital products offer high margins and instant delivery. Once created, they can be sold repeatedly with minimal additional cost.
Examples include:
-
Online courses
-
E-books and templates
-
Software licenses
-
Digital tools and assets
This revenue model is highly scalable and well-suited to knowledge-based e-businesses.
Advertising and Sponsored Revenue
Some electronic commerce platforms generate revenue through advertising. This is common for high-traffic websites and marketplaces.
Advertising revenue may include:
-
Sponsored product listings
-
Display advertising
-
Brand partnerships
-
Featured placements
This model works best when platforms attract consistent and engaged traffic.
Affiliate Revenue Models
Affiliate marketing allows businesses to earn commissions by promoting third-party products.
Key benefits:
-
No inventory management
-
Low operational costs
-
Performance-based earnings
Affiliate revenue often complements other models rather than serving as the sole income source.
Freemium and Upsell Strategies
Freemium models offer basic services for free while charging for advanced features. Upselling encourages customers to purchase higher-value options.
This approach:
-
Lowers entry barriers for new users
-
Increases conversion opportunities
-
Boosts average order value
Freemium strategies are common in digital commerce and software-driven platforms.
Combining Multiple Revenue Models
Many successful companies in the electronic commerce industry use hybrid revenue models.
Common combinations include:
-
Product sales + subscriptions
-
Marketplace commissions + advertising
-
Digital products + affiliate income
Diversifying revenue streams reduces risk and improves financial stability.
Choosing the Right Revenue Model
The best revenue model depends on several factors:
-
Target audience behavior
-
Product or service type
-
Operational capacity
-
Growth objectives
Testing and refining revenue strategies over time helps businesses remain competitive.
Common Revenue Model Mistakes to Avoid
Businesses often struggle due to poor revenue planning.
Avoid these mistakes:
-
Relying on a single revenue source
-
Ignoring profit margins
-
Underpricing products or services
-
Scaling before validating the model
A well-tested revenue model supports sustainable growth.
Conclusion
The electronic commerce industry is powered by diverse and evolving revenue models. From direct product sales and subscriptions to marketplaces and digital products, each model offers unique advantages.
Businesses that understand and strategically implement the right revenue models are better positioned to grow profitably. In a competitive digital landscape, revenue design is as important as product quality and marketing.